An ovarian cyst is a sac filled with fluid or semisolid material that forms on or within one or both of your ovaries. Your ovaries are small organs in your pelvis that hold egg cells and make hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone.
There are different types of ovarian cysts, most of which are painless and harmless (benign). Usually, ovarian cysts don’t cause symptoms. You likely won’t know you have one unless your provider finds one during a routine pelvic exam or imaging procedure.
Rarely, ovarian cysts can cause complications. Scheduling regular pelvic exams and speaking with your provider about any symptoms you may be experiencing can help prevent any problems with a cyst.
Most ovarian cysts cause no symptoms and go away on their own. But a large ovarian cyst can cause:
Most ovarian cysts form as a result of your menstrual cycle. These are called functional cysts. Other types of cysts are much less common.
Your ovaries grow small cysts called follicles each month. Follicles produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone and break open to release an egg when you ovulate.
A monthly follicle that keeps growing is known as a functional cyst. There are two types of functional cysts:
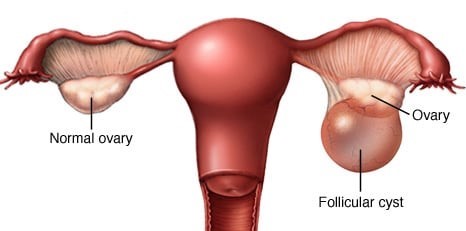
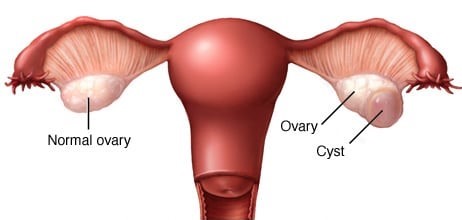
Functional cysts are usually harmless. They rarely cause pain and often disappear on their own within 2 to 3 menstrual cycles.

HealthNeutron is a preventive healthcare provider and digital healthcare solution that brings doctors, lab technicians, and pharmacists to patients.
HealthNeutron © 2024 | All Rights Reserved.
Made with ❤️ by Pearson Consultancy