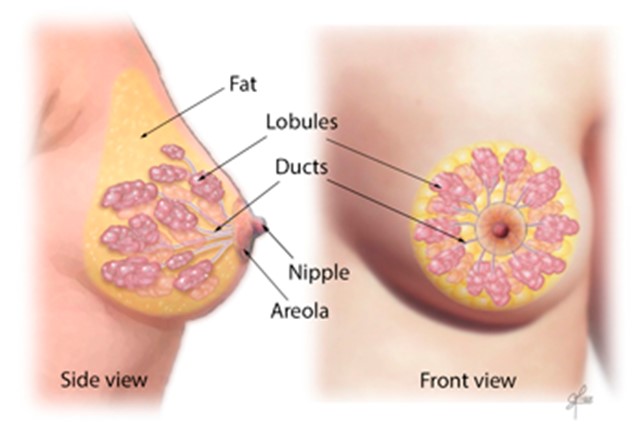
The most common types of breast cancer are-
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. The cancer cells begin in the ducts and then grow outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Cancer cells begin in the lobules and then spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
There are several other less common kinds of breast cancer, such as Paget’s disease, medullary, mucinous, and inflammatory breast cancer.
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a breast disease that may lead to invasive breast cancer. The cancer cells are only in the lining of the ducts and have not spread to other tissues in the breast.
Causes
Doctors know that breast cancer occurs when some breast cells begin to grow abnormally. These cells divide more rapidly than healthy cells do and continue to accumulate, forming a lump or mass. Cells may spread (metastasize) through your breast to your lymph nodes or to other parts of your body.
Breast cancer most often begins with cells in the milk-producing ducts (invasive ductal carcinoma). Breast cancer may also begin in the glandular tissue called lobules (invasive lobular carcinoma) or in other cells or tissue within the breast.
Researchers have identified hormonal, lifestyle, and environmental factors that may increase your risk of breast cancer. But it’s not clear why some people who have no risk factors develop cancer, yet other people with risk factors never do. It’s likely that breast cancer is caused by a complex interaction of your genetic makeup and your environment.
Inherited breast cancer
Doctors estimate that about 5 to 10 percent of breast cancers are linked to gene mutations passed through generations of a family.
A number of inherited mutated genes that can increase the likelihood of breast cancer have been identified. The most well-known are breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) and breast cancer gene 2 (BRCA2), both of which significantly increase the risk of both breast and ovarian cancer.
If you have a strong family history of breast cancer or other cancers, your doctor may recommend a blood test to help identify specific mutations in BRCA or other genes that are being passed through your family.
Consider asking your doctor for a referral to a genetic counselor, who can review your family health history. A genetic counselor can also discuss the benefits, risks, and limitations of genetic testing to assist you with shared decision-making.